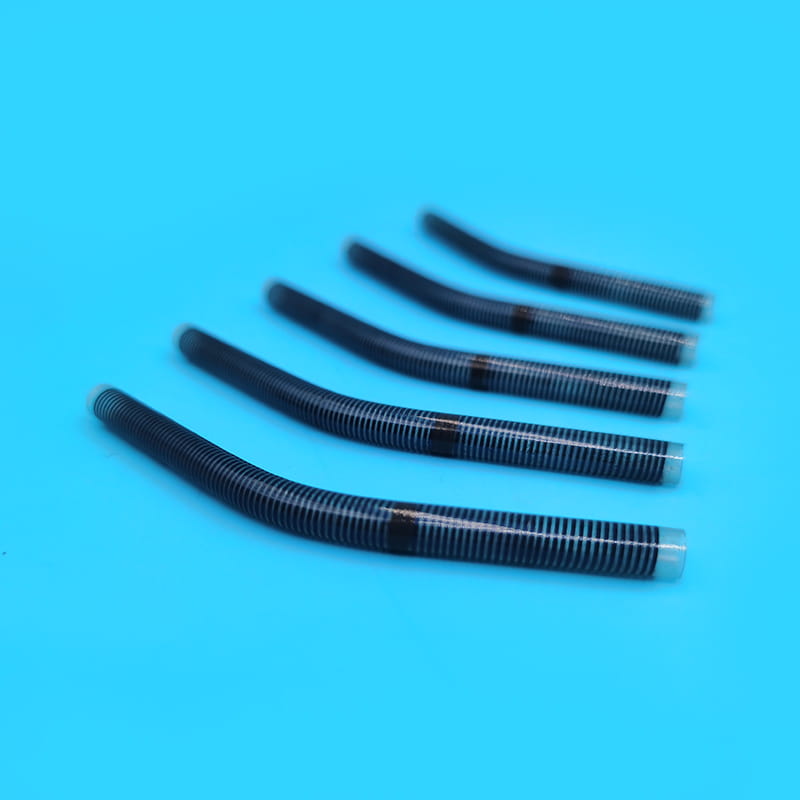
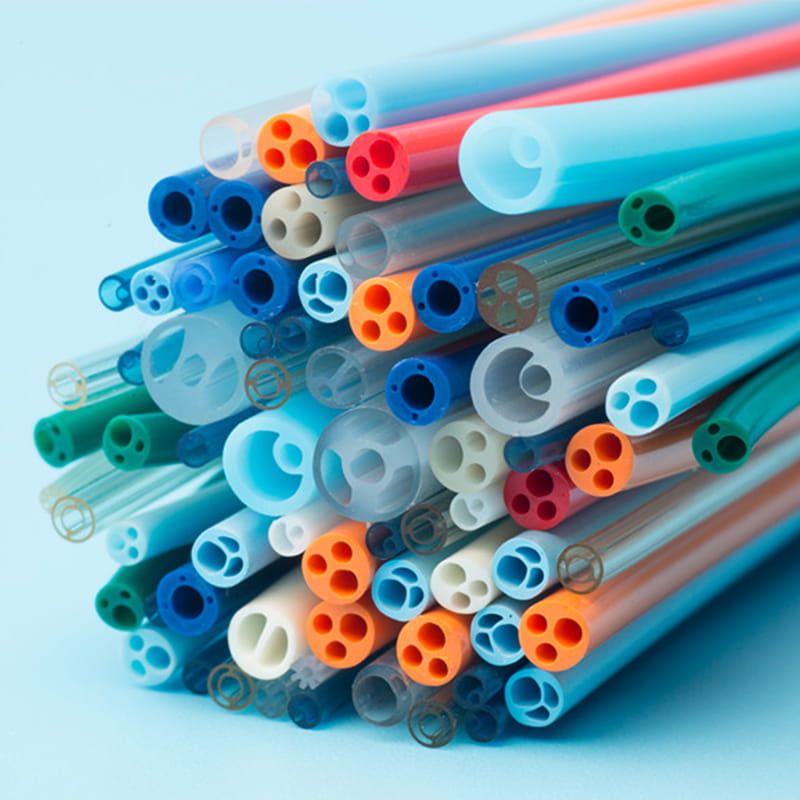
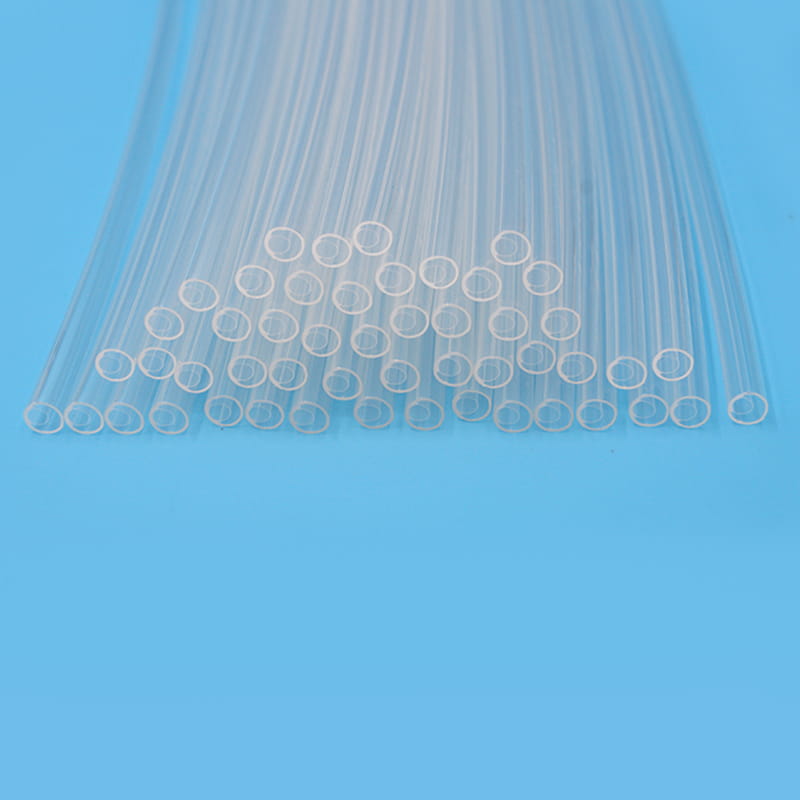
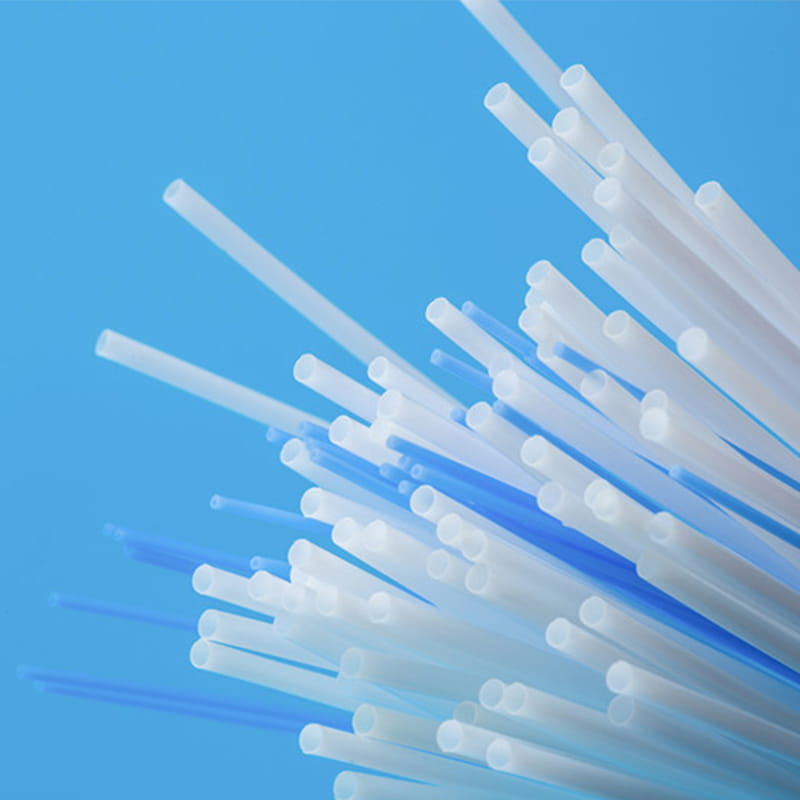
Medical TPU tube is a kind of rubber tube used for medical purposes
Medical TPU tube is a kind of rubber tube used for medical purposes. Due to the excellent properties of the material itself, the minimum inner diameter of the tube can reach 0.4 mm. The material has passed the biocompatibility test and has little reaction to human tissue. It will not cause foreign body reaction after implantation in human tissue, and will not cause inflammation to surrounding tissues. Even the tube has no abnormal reaction after being placed in the human body for 30 days, so it is widely favored by the medical industry.
Features
As a medical catheter product, its performance is naturally not bad. This type of catheter is often inserted into the human body, and its chemical properties are extremely stable and non-toxic and non-irritating to the human body. Not only that, this catheter is resistant to weak acids and alkalis, has high transparency, and is convenient for transporting various medical liquids.
Since it is a hose, its elasticity is naturally not bad. It has a soft texture, good elasticity, is resistant to kinks and deformation, and has excellent resilience. At low temperatures, the tube will not harden and lose its elasticity; at high temperatures, the tube will not oxidize and become hard and yellow. The working environment temperature is between minus 50 and 150 degrees Celsius.
Excellent insulation, it can be sterilized with ethylene oxide under high temperature conditions. It complies with the food and drug testing standards, does not turn yellow, frost, whiten, or fade at room temperature, and does not scale after being placed in water for a long time.
Process
Extrusion molding: Install the mold on the head of the extruder. After dehumidification and drying, the purpose is to prevent bubbles and bulges during the extrusion process. Then feed the material through the extruder, extrude and shape it, vacuum shape it, cool it, pull it, cut it off, and collect it.
The following are some pictures of our company's medical catheters:
The above products are just for display, and our company can customize catheters according to customer requirements
Application areas
Food and medical machinery, medical diversion, biopharmaceuticals, medical research, medical analysis instruments, hemostasis instruments, biological research institutes, chemical laboratories
TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer) is a thermoplastic elastomer material.
PVC (Polyvinyl chloride) is an amorphous polyvinyl chloride material.
Introduction to TPE material characteristics: TPE has the characteristics of high strength, high resilience, injection molding, wide application range, environmental protection, non-toxic and safe, and excellent colorability. It has a soft touch, weather resistance, fatigue resistance and temperature resistance, excellent processing performance, no need for vulcanization, can be recycled to reduce costs, can be secondary injection molded, coated and bonded with base materials such as PP, PE, PC, PS, ABS, etc., or can be molded alone.
Introduction to the characteristics of PVC materials:
PVC has excellent electrical properties, strong acid and alkali resistance, good chemical stability, but low softening point. It is suitable for making thin plates, wire and cable insulation layers, seals, etc.
Amorphous materials, low moisture absorption, poor fluidity. In order to improve fluidity and prevent bubbles, the plastic can be dried in advance. The mold casting system should be short and thick, the gate section should be large, and there should be no dead corners. The mold must be cooled and the surface must be chrome-plated.
Pebax is a nylon elastomer, an engineering polymer, with a fairly wide hardness range and good resilience, as well as outstanding low-temperature impact resistance, corrosion resistance to most chemicals, and excellent anti-aging and sunlight exposure capabilities. These properties make Pebax elastic materials widely used in various fields, including medical devices, medical extrusion (tubes) can be divided into stent balloon tubes, braided reinforced tubes (delivery systems), multi-lumen tubes (guidewires, liquids, gases, etc. can be passed through the lumen), intravenous catheters, high-performance materials, and due to different designs, there will be co-extruded tubes, reducer tubes, tip tubes, pigtail tubes and other reprocessed catheters. Medical-grade extrusion is also widely used. In terms of materials, the medical-grade materials involved are: Pebax®, Nylon (nylon), PC (polycarbonate), PP (polypropylene), TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane), PVC (polyvinyl chloride), PE (polyethylene), HDPE (high-density polyethylene), LDPE (low-density polyethylene),
3. A Fei:
Tracheal intubation is anesthesia, a method often used to keep the airway open during the rescue and re-monitoring of critically ill patients. It is the most widely used and most convenient method in clinical general anesthesia and respiratory management.
Inserting the endotracheal tube too deep or too shallow may cause serious accidents. Too shallow may cause the tube to fall off and glottis to be injured, while too deep may cause the tube to be inserted into the bronchus, leading to regurgitation, hypoxemia, dyspnea, arrhythmia and other consequences, which will directly affect the rescue and operation, and even endanger the patient's life safety.
Unplanned endoracheal extubation (UEX) is an important safety indicator of the quality of ICU and hospital nursing, and is also one of the more common serious complications in clinical nursing. Unplanned extubation can lead to a series of serious complications, prolong the time of mechanical ventilation and ICU stay, and increase medical costs. The mortality rate of patients who need to be re-cannulated after UEX can reach 25%. Improper UEX treatment can also cause medical correction. Early prevention is important for accident handling. The rapid identification of the location and depth of endotracheal intubation is very important for general anesthesia surgery, clinical rescue, and ICU nursing. Early detection and prevention are important for identifying whether the artificial airway is successfully established, which is the key to reducing various risks and complications. Clinical data show that early prevention with convenient identification is significantly better than accident handling in reducing risks.
Due to changes in body position, transfer of patients, and major errors in exploration, the catheter may be inserted too deep or too shallow, which may lead to serious consequences: if it is inserted too deep, it will cause the lungs to become suspended near the airway, increase the airway resistance, and even hypoxia, which may endanger the patient's life; if it is inserted too shallowly, it will cause the catheter to fall out of the trachea and cause hypoxia and vacuity, which is life-threatening. Therefore, it is very important to find out in time whether the catheter is inserted too deep or too shallow.
With the help of simple and effective color code recognition, medical staff can find abnormal catheterization early and prevent UEX from happening. Its safety
cannot be replaced by post-treatment of equipment.
2. Scope of clinical application
Department of Anesthesiology
Department of Emergency
Common name: balloon dilatation catheter


The (Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty) catheter is a double-lumen catheter with a balloon (PA12) located near the distal tip of the catheter. One lumen of the catheter is used to fill the balloon, and the outlet of the lumen is located in the side branch portion of the catheter tail. The other lumen starts from the straight entrance at the tail end of the catheter, through which a guidewire (maximum diameter 0.035'') can be inserted and advanced to the distal end of the catheter and pressure monitoring can be performed. The balloon has two radiopaque markers for locating the relative position of the balloon and the stenotic segment of the blood vessel. The radiopaque marker band can indicate the dilated portion of the balloon and can assist in balloon placement. The product is electron beam sterilized and is for single use.

A balloon dilatation catheter is a soft catheter with an inflatable balloon at the tip, which is used to dilate narrow hollow organs in the human body, such as blood vessels, digestive tract, urinary tract, etc., under image guidance. Without expansion, the balloon catheter enters the target lesion site. After successful treatment, the balloon can be retracted to withdraw the balloon catheter out of the body. Several basic characteristics of vascular dilatation balloons are as follows: balloon compliance and expansion force → circumferential stress → balloon cross-sectional area → tracking force → anti-bending property → pushability → balloon catheter head → balloon expansion and contraction times → other functions of balloon PTA catheter

In the balloon In the less than 20 years since the advent of balloon angioplasty, balloon catheter and guidewire technology has continued to advance based on clinical needs and market competition. Modern peripheral PTA balloon catheters have high pressure, low flexibility, limited flexibility, small cross-section, steerable, pushable, and (for some balloons) scratch-resistant properties.




Ureteroscopic balloon dilatation catheters include balloon dilatation catheters and pressure pumps (some models). The catheter of the ureteroscopic balloon dilatation catheter is made of materials such as polyimide (PI), and the balloon part is made of materials such as PET, PE, Pebax, etc. Ethylene oxide sterilization, the product is disposable.

Indications: Catheters used for percutaneous transluminal angioplasty are suitable for the treatment of stenosis and dilatation of the following blood vessels, including but not limited to: lower extremities, pelvis, kidneys.
For more information, please call us at +86-18913710126 or email us at [email protected].
The medical industry is increasingly relying on advanced materials for various applications, and one...
A medical balloon catheter is a sophisticated medical device designed to perform a variety of proced...
Introduction The TPU Reducer Tube (Thermoplastic Polyurethane Reducer Tube) is a versatile and high-...
In modern medicine, medical catheters are indispensable tools used in a wide range of treatments and...
In the healthcare industry, the importance of selecting the right materials for medical devices cann...
In the era of precision medicine, a small tube often carries the weight of life-saving responsibilit...